Introduction
The world is becoming increasingly digital. We are relying more on digital platforms as from online banking to remote work, shopping to education. With this convenience however comes the growing threat of cybercrime. Cyber-attacks are no longer limited to big corporations even anyone with an internet connection can be a target. That’s where Cyber Security comes in.
Cyber Security is essential to protect personal data, financial information, intellectual property and critical infrastructure. In this post we’ll explore what cyber security is, dive into the types of cyber security and break down common terms every internet user should understand.
What is Cyber Security?
Cyber Security refers to the practice of protecting systems, networks, devices and data from cyber threats such as unauthorized access, data breaches or digital attacks. It is a broad field that encompasses technologies, processes and practices designed to defend against both external and internal threats.
Cyber Security is also known by other names like:
- Information Security (InfoSec)
- IT Security
- Computer Security
Primary goal is to maintain confidentiality, integrity and availability of digital information—a principle often referred to as the CIA Triad.
Types of Cyber Security
Cyber security is a vast field that covers various domains. Here is the main types of cyber security that protect different aspects of the digital ecosystem:
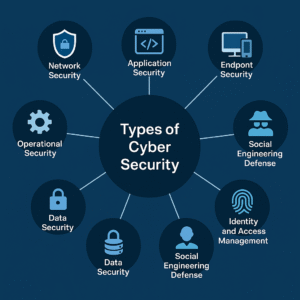
- Network Security
Network security involves protecting internal networks from intruders by securing both hardware and software technologies. It includes firewalls, intrusion detection systems (IDS), antivirus programs and VPNs.
Key features:
- Controlled incoming and outgoing traffic
- Detects suspicious activity
- Prevent unauthorized access
Example: Blocks hackers IP address trying to access your router.
- Application Security
This focus on keeping software and devices free of threats. Applications must be updated and tested on regular bases for vulnerabilities to prevent exploits.
Techniques include:
- Code reviews
- Vulnerability scanning
- Patching software bugs
Example: Fixing of flaws in web apps to avoid SQL injection.
- Endpoint Security
Endpoints are devices like laptops, desktops and mobile phones. Endpoint security protects these devices from being exploited in network.
Tools used:
- Antivirus
- Endpoint Detection and Response (EDR)
- Device encryption
Example: Installation of antivirus software’s on an employee laptops to prevent malware.
- Cloud Security
Cloud security protects data stored online through cloud computing platforms like AWS, Google Cloud or Microsoft Azure. It involves encryption, identity management and secure configurations.
Cloud threats include:
- Data leaks
- Misconfigurations
- Insecure APIs
Example: access control is used to prevent unauthorized users from viewing private files that is stored in Google Drive.
- Social Engineering Defense
Social engineering exploits human behavior instead of technical ambiguities. Examples include phishing emails, fake tech support calls and pretexting.
Defensive measures:
- User training
- Email filtering
- Awareness campaigns
Example: Teach employees how to identify suspicious mails.
- Identity and Access Management (IAM)
IAM ensures that right people access the right resources at the right time for the right reasons.
Includes:
- Role-based access control
- Multi-factor authentication (MFA)
- Single Sign-On (SSO)
Example: Use finger prints for authentication to access sensitive data on a mobile apps.
- Data Security
This area involves protecting digital information from corruption, theft or loss. It includes data encryption, masking and proper storage.
Common data security threats:
- Ransom ware
- Insider threats
- Data losses due to hardware failure
Example: Encryption of data to ensure safety in a database.
- Operational Security
Operational security (OpSec) handles policies and decisions for handling and protecting data assets. It includes permissions and access levels, audits and compliance with regulations as GDPR or HIPAA.
Example: Restrict access of payroll to only the HR department.
Cyber Security Terminology
If you’re new to cyber security then it can be confusing. Here is a quick breakdown of terms used commonly:
Firewall
A system that filters incoming and outgoing traffic based on pre-defined rules.
Malware
Short for “malicious software,” this includes viruses, Trojans, worms, ransom ware and spyware.
Phishing
A fraudulent attempt to access sensitive data as passwords or credit card info by disguising as a trustworthy entity.
Encryption
The process of converting data into a coding format to secure unauthorized access.
Patch
A software updates that fixes vulnerabilities or bugs.
Zero-Day
A software flaws unknown to the vendor, which hackers can exploit before it is fixed.
Ransom ware
A Malicious software that hacks your data or device to demand payments for unlock.
DDoS (Distributed Denial of Service)
An attack that over loads a system with malicious traffic, cause it to crash or become unavailable.
Threat Actor
An individual or group is responsible for a cyber-attack.
Two-Factor Authentication (2FA)
An added layer of security requires two types of credential to verify identity (e.g. password + phone code).
How to Get Started with Cyber Security
If you’re interested in diving deep, here is a few tips:
- Stay Updated: Follow cyber security blogs, pod casts and news outlets
- Learn the Basics: Sites as TryHackMe, HackTheBox, or Coursera offers beginner friendly paths
- Use Tools: Try free tools as Wireshark, Nmap or Burp Suite in a virtual labs
- Consider Certifications: If you interested about career then start with CompTIA Security or CEH
Conclusion
Cyber Security is no more optional—it’s mandatory. You are an individual trying to protect your online presence or a business owner safe guarding your data, understanding the different types of cyber security and common terminology gives you the upper hand. Educate yourself and implement best practices, you become part of the global efforts to build a safe digital world.