Today’s digital era, cloud computing is the invisible backbone of nearly every app, website and online service that we use as from Netflix streaming to Gmail, from banking platforms to AI driven analytics. What is exactly cloud computing, how does it work and why is it so crucial?
This guide deep dives into cloud computing, its core types and the three foundational service models as IaaS, PaaS and SaaS.
What is Cloud Computing?
Cloud computing is the delivery of computing services including storage, processing power, databases, networking, software and analytics—over the internet (the “cloud”) rather than relying on local servers or personal computers.
Key Characteristics:
- On demand access: resources are available when needed
- Scalability: As per demand resources can be increased or decreased
- Pay as you go model: Pay for what you use only
- Global accessibility: with internet connection access your resources from anywhere
Why Cloud Computing is Important?
- Reduces capital cost on hardware
- Fast deployment of updates and apps
- Powers real time collaboration for remote teams
- Supports innovation with tools as machine learning, IoT and big data
- Increases disaster recovery time and guaranties up time
Cloud computing empowers businesses of all sizes to innovate fast, reduce IT cost and scale seamlessly, making it an important component of modern infrastructure.
Types of Cloud Computing: (Deployment Models)
Cloud computing is categorized into four deployment models based on, how infrastructure is deployed and accessed:
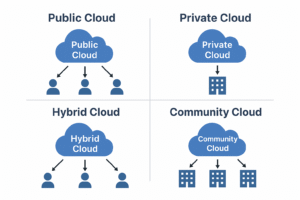
- Public Cloud
The public cloud is operated by third party cloud providers (e.g. AWS, Azure and Google Cloud) that deliver services over the internet.
- Examples: Amazon Web Services (AWS), Microsoft Azure and Google Cloud Platform (GCP)
- Users: Startups, SMBs, enterprises and developers
Benefits:
- Low upfront cost
- High scalability
- Managed infrastructure
Drawbacks:
- Limited customization
- Shared resources (multi-tenancy)
- Possibility of data residency issues
- Private Cloud
A private cloud is used by a single organization exclusively and can be hosted on premise or in a third party data center.
- Examples: VMware, OpenStack and Microsoft Azure Stack
- Users: Government agencies, financial institutions and large enterprises
Benefits:
- Full control over infrastructure
- compliance and security increased
- Custom configurations
Drawbacks:
- Higher costs
- Requires skilled IT teams
- Hybrid Cloud
Hybrid cloud combines public and private cloud, enabling data and apps to move between them.
- Examples: Azure Arc, Google Anthos and AWS Outposts
- Users: Enterprises with both regulated and non regulated workloads
Benefits:
- Flexibility and scalability
- Risk mitigation (e.g. sensitive data is stored in private cloud)
- Disaster recovery and backup advantages
Drawbacks:
- Management and setup complexity
- Integration challenges
- Community Cloud
A community cloud is shared among organizations with similar requirements (e.g. regulatory and security).
- Examples: Government consortium and healthcare networks
- Users: Sector with shared mission and compliance need
Benefits:
- Cost benefits for use cases
- Tailored compliance and governance
Drawbacks:
- Limited scalability
- Less flexible than public cloud
Cloud Computing Service Models
There are three main cloud service models, each offering different levels of control, flexibility and management:
- IaaS: (Infrastructure as a Service)
IaaS provides virtualized computing infrastructure on the internet that is servers, storage and networking. Users manage their applications and operating systems and provider manages the hardware.
- Examples: Amazon EC2, Microsoft Azure VMs and Google Compute Engine
- Users: System administrators, DevOps teams and web developers
Benefits:
- control and High flexibility
- Scalable on demand
- Cost effective for dynamic workload
Drawbacks:
- Technical expertise required
- Users must manage security update and patches
- PaaS (Platform as a Service)
PaaS provides a platform with tools to develop, test and deploy applications. The provider manages the infrastructure, OS and runtime environment.
- Examples: Google App Engine, Microsoft Azure App Services and Heroku
- Users: Developers and software engineers
Benefits:
- Simplify deployment and scaling
- Focus on code, not on infrastructure
- Built in development tools and API’s
Drawbacks:
- Less control over the environment
- Possible vendor lock-in
- SaaS (Software as a Service)
SaaS delivers fully functional applications on the web. Users access apps via browser without worrying about infrastructure or its maintenance.
- Examples: Gmail, Microsoft 365, Dropbox and Zoom
- Users: End users, businesses and consumers
Benefits:
- Zero installation and maintenance
- Subscription based pricing
- Accessible from anywhere
Drawbacks:
- Limited customization
- Data resides on the provider’s cloud
Comparison the Cloud Service Models
Feature IaaS PaaS SaaS
Managed By You You + Provider Provider
Example Users IT admins, DevOps, Developers and End users
Customization High Moderate Low
Example Services AWS EC2, Azure VMs, Google App Engine, Heroku, Gmail and Office 365
Use Case Hosting web servers, developing web apps, using email or CRM tools
Key points:
- Types (Deployment Models): Public, Private, Hybrid and Community
- Services Model: IaaS (flexibility), PaaS (developers speed) and SaaS (ease of use)
- Choose the right combination based on business goals, budget and expertise.
Final Thoughts
Cloud computing is no longer optional. It is strategically enabler for agility, scalability and innovation. Whether you’re a developer hosting an app, an enterprise architect building hybrid model or a student learning to deploy containers, understanding the types of cloud and its services model is a foundation to your success.